Research Resources

MEET: A Million-Scale Dataset for Fine-Grained Geospatial Scene Classification with Zoom-Free Remote Sensing Imagery
IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 1004–1023, May 2025.
Yansheng Li, Yuning Wu, Gong Cheng, Chao Tao, Bo Dang, Yu Wang, Jiahao Zhang, Chuge Zhang, Yiting Liu, Xu Tang, Jiayi Ma, and Yongjun Zhang
Accurate fine-grained geospatial scene classification using remote sensing imagery is essential for a wide range of applications. However, existing approaches often rely on manually zooming remote sensing images at different scales to create typical scene samples. This approach fails to adequately support the fixed-resolution image interpretation requirements in real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we introduce the Million-scale finE-grained geospatial scEne classification dataseT (MEET), which contains over 1.03 million zoom-free remote sensing scene samples, manually annotated into 80 fine-grained categories. In MEET, each scene sample follows a scene-in-scene layout, where the central scene serves as the reference, and auxiliary scenes provide crucial spatial context for fine-grained classification. Moreover, to tackle the emerging challenge of scene-in-scene classification, we present the Context-Aware Transformer (CAT), a model specifically designed for this task, which adaptively fuses spatial context to accurately classify the scene samples. CAT adaptively fuses spatial context to accurately classify the scene samples by learning attentional features that capture the relationships between the center and auxiliary scenes. Based on MEET, we establish a comprehensive benchmark for fine-grained geospatial scene classification, evaluating CAT against 11 competitive baselines....
[Dataset] | [related publications] | [code]
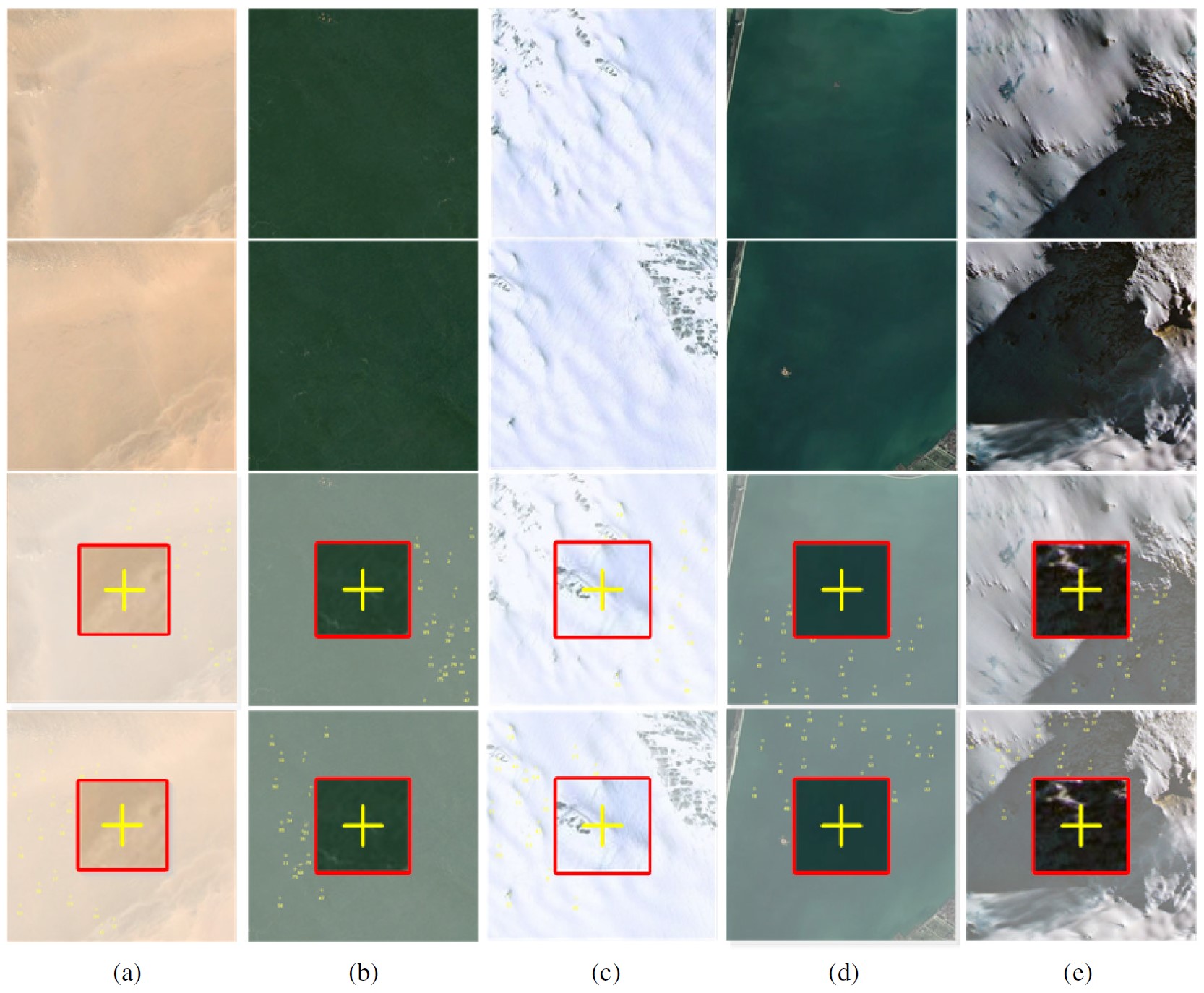
Weak texture remote sensing image matching based on hybrid domain features and adaptive description method
The Photogrammetric Record, 38(184):537-62, Dec 2023.
Wupeng Yang, Yongxiang Yao, Yongjun Zhang*, Yi Wan
Weak texture remote sensing image (WTRSI) has characteristics such as low reflectivity, high similarity of neighbouring pixels and insignificant differences between regions. These factors cause difficulties in feature extraction and description, which lead to unsuccessful matching. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel hybrid-domain features and adaptive description (HFAD) approach to perform WTRSI matching. This approach mainly provides two contributions: (1) a new feature extractor that combines both the spatial domain scale space and the frequency domain scale space is established, where a weighted least square filter combined with a phase consistency filter is used to establish the frequency domain scale space; and (2) a new log-polar descriptor of adaptive neighbourhood (LDAN) is established, where the neighbourhood window size of each descriptor is calculated according to the log-normalised intensity value of feature points...
[Dataset] | [related publications]
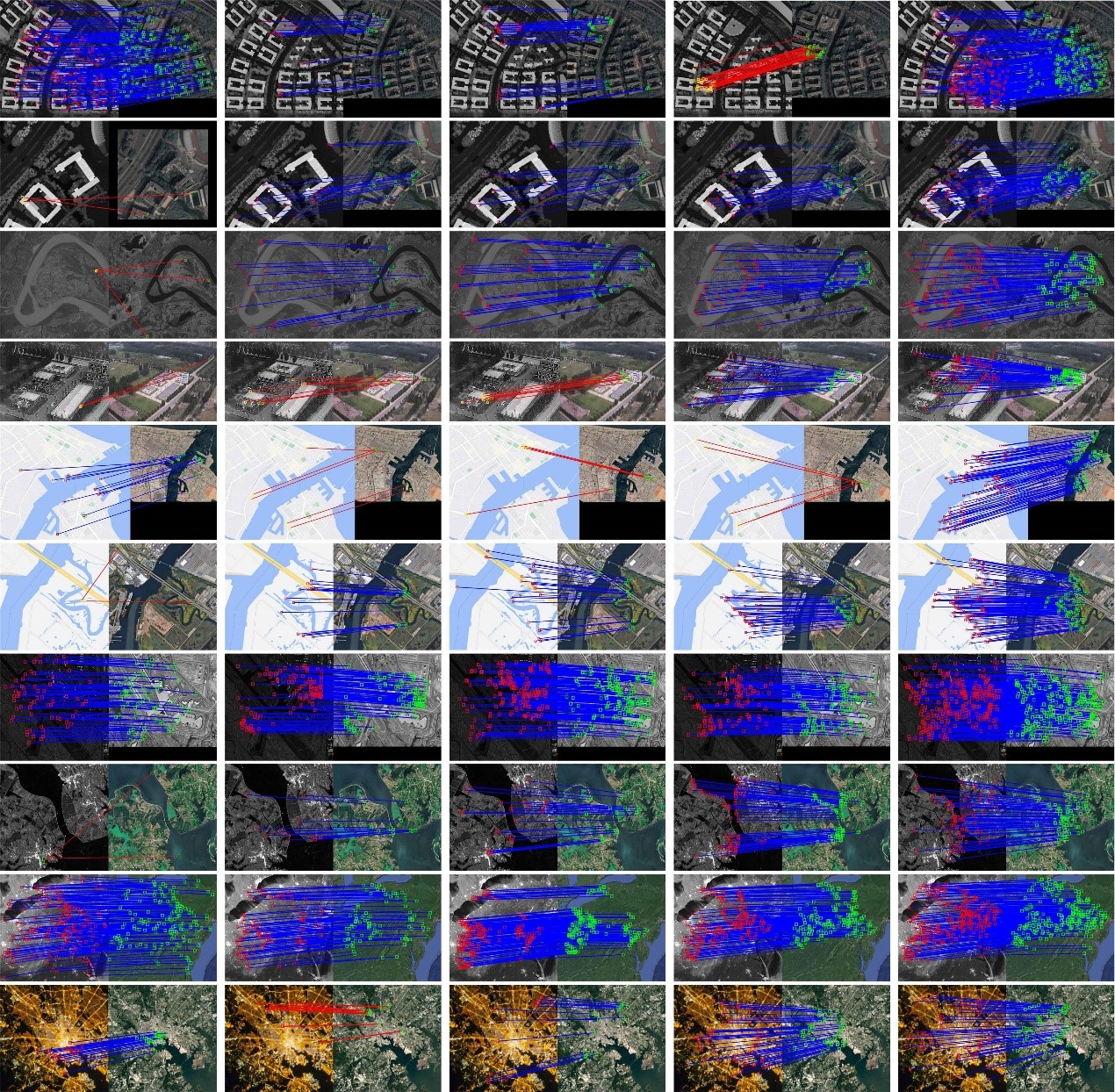
Histogram of the orientation of the weighted phase descriptor for multi-modal remote sensing image matching
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 196:1-5, Feb 2023.
Yongjun Zhang*, Yongxiang Yao, Yi Wan*, Weiyu Liu, Wupeng Yang, Zhi Zheng, and Rang Xiao
Multi-modal remote sensing image (MRSI) has nonlinear radiation distortion (NRD) and significant contrast differences to which image gradient features are usually sensitive. Although image phase features are more robust against NRD, they might not be much helpful in resolving the problems of directional inversion or phase extreme value mutations that are common in the phase feature calculation. To address these issues, a new MRSI matching method—"histogram of the orientation of weighted phase” (HOWP)—is proposed in this paper. This method distinguishes itself from other methods in three aspects: (1) a feature aggregation strategy is used to optimize feature points by extracting the corner and blob features separately; (2) a novel weighted phase orientation model is established to replace the traditional image gradient orientation features; and (3) a regularization-based log-polar descriptor is constructed to generate robust feature description vectors...
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]
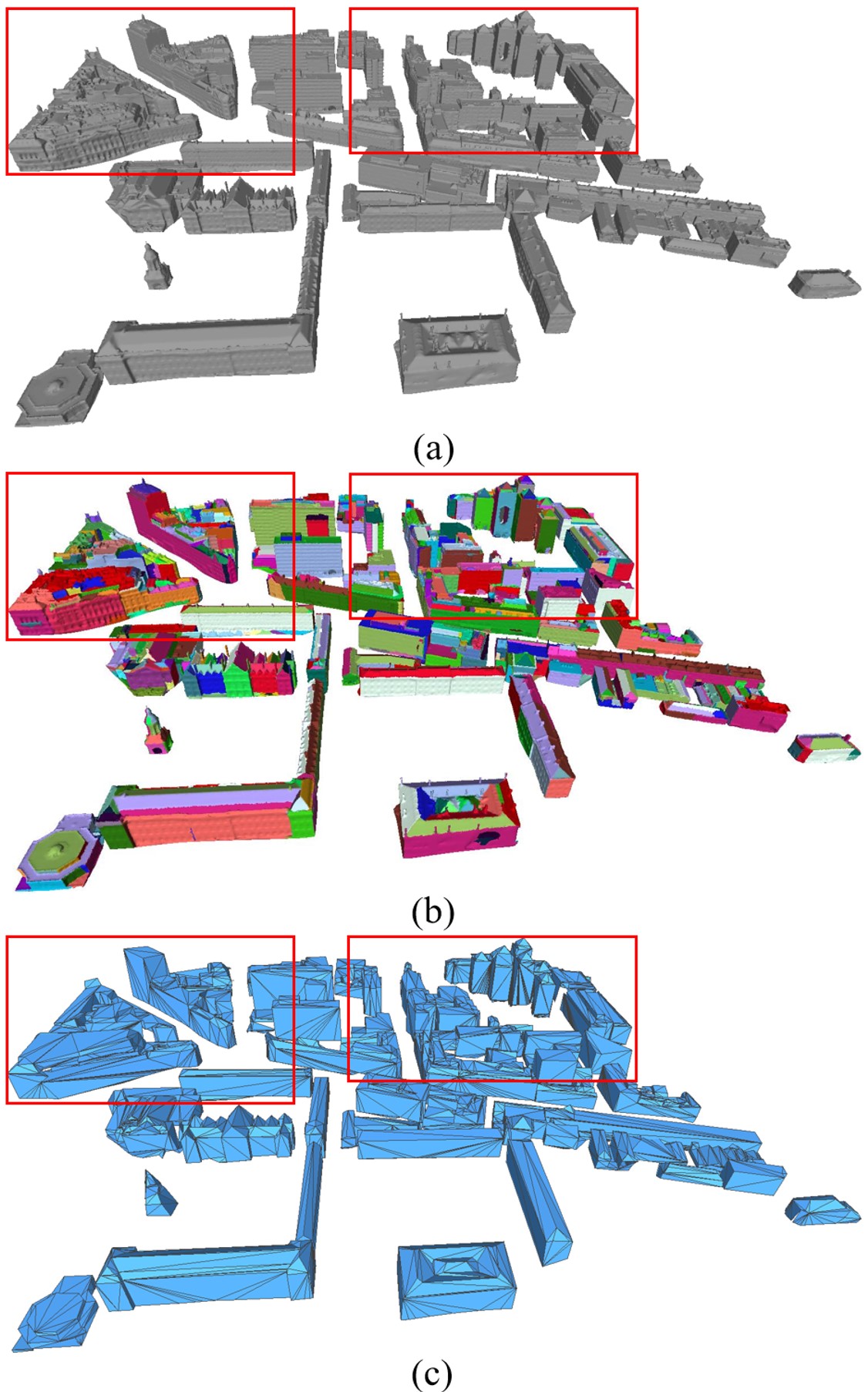
Generation of Concise 3D Building Model from Dense Meshes by Extracting and Completing Planar Primitives
The Photogrammetric Record, 38(181):22-46, Mar 2023.
Xinyi Liu, Xianzhang Zhu*, Yongjun Zhang*, Senyuan Wang and Chen Jia
The generation of concise building model has been and continues to be a challenge in photogrammetry and computer graphics. The current methods typically focus on the simplicity and fidelity of the model, but those methods either fail to preserve the structural information or suffer from low computational efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel method to generate concise building models from dense meshes by extracting and completing the planar primitives of the building. From the perspective of probability, we first extract planar primitives from the input mesh and obtain the adjacency relationships between the primitives. Since primitive loss and structural defects are inevitable in practice, we employ a novel structural completion approach to eliminate linkage errors. Finally, the concise polygonal mesh is reconstructed by connectivity-based primitive assembling. Our method is efficient and robust to various challenging data. Experiments on various building models revealed the efficacy and applicability of our method..
[Dataset] | [related publications]
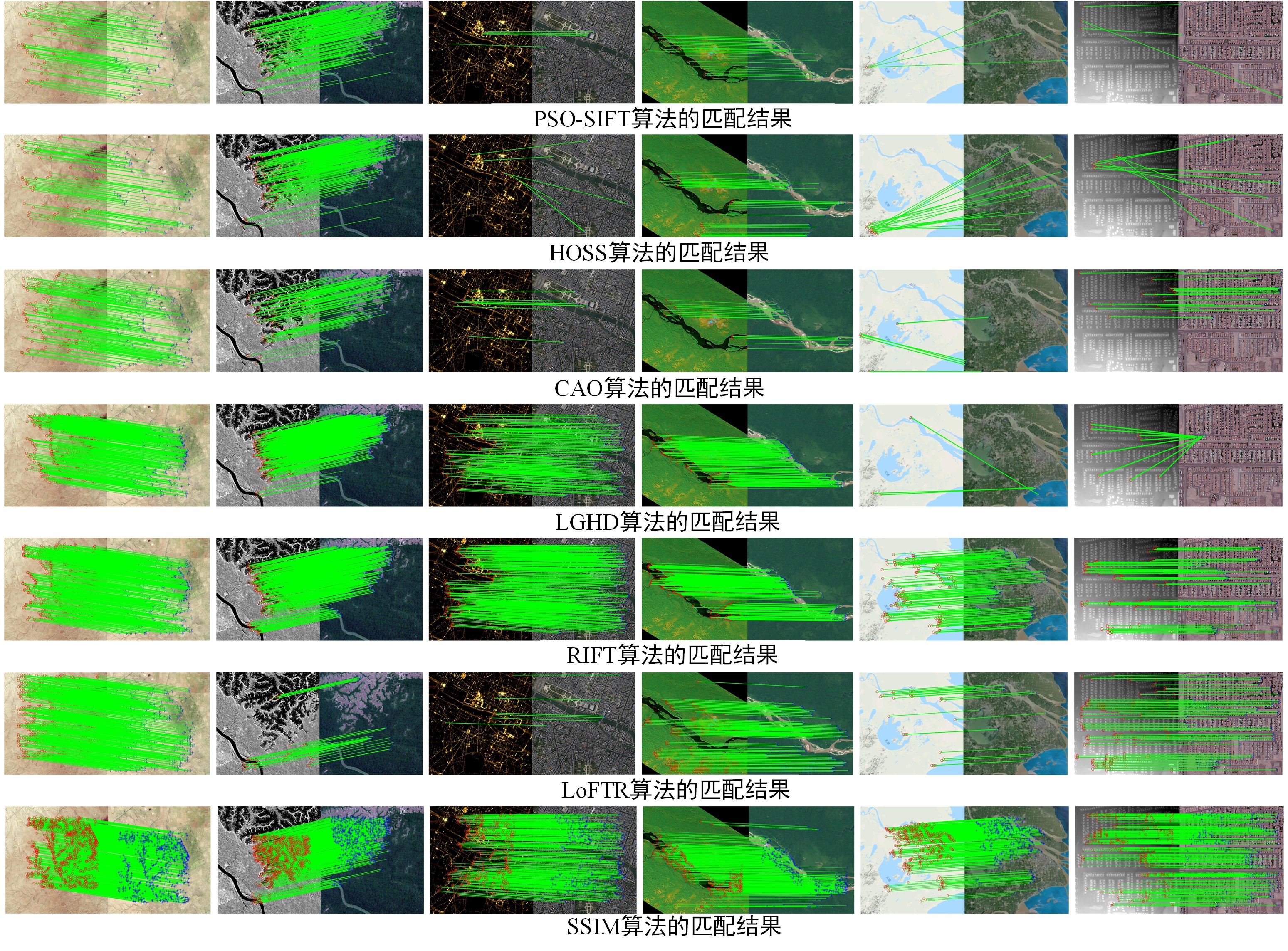
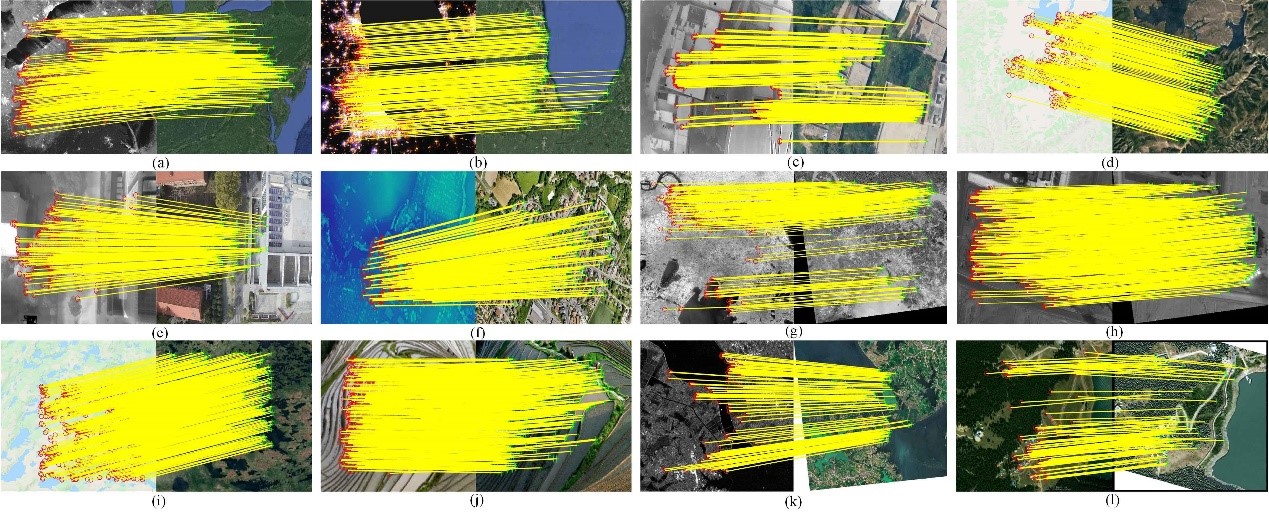
SIMD: Self-similarity Index Map for Multi-modal Remote Sensing Image Matching
Yongxiang Yao, Yi Wan, Yongjun Zhang, Bin Zhang, Siyuan Zou and Wupeng Yang
Geometric registration with point matches is the key to multi-modal remote sensing data fusion. However, the different imaging mechanisms of multi-modal remote sensing images (MRSIs) can lead to serious non-linear radiation distortion and significant differences in texture details, making the matching of MRSIs very difficult. In this paper, we propose a novel self-similarity index map (SSIM) based on the MRSI matching method...
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]
MoTIF: Multi-orientation tensor index feature descriptor for SAR-optical image registration
The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. 2022 May 30;43:99-105.
Yongxiang Yao, Bin Zhang, Yi Wan and Yongjun Zhang
The inherent speckle noise in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and the significant differences between SAR and optical images in nonlinear radiation give rise to the great difficulty in computing similarity between image features, improving detection accuracy of corresponding points and the efficiency of image matching, thus making the registration of SAR and optical images a long-standing challenging task. To address these issues, a new SAR-optical image registration method was proposed in this paper, namely, Multi-orientation Tensor Index Feature (MoTIF), which is characterized by a lightweight feature descriptor....
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]
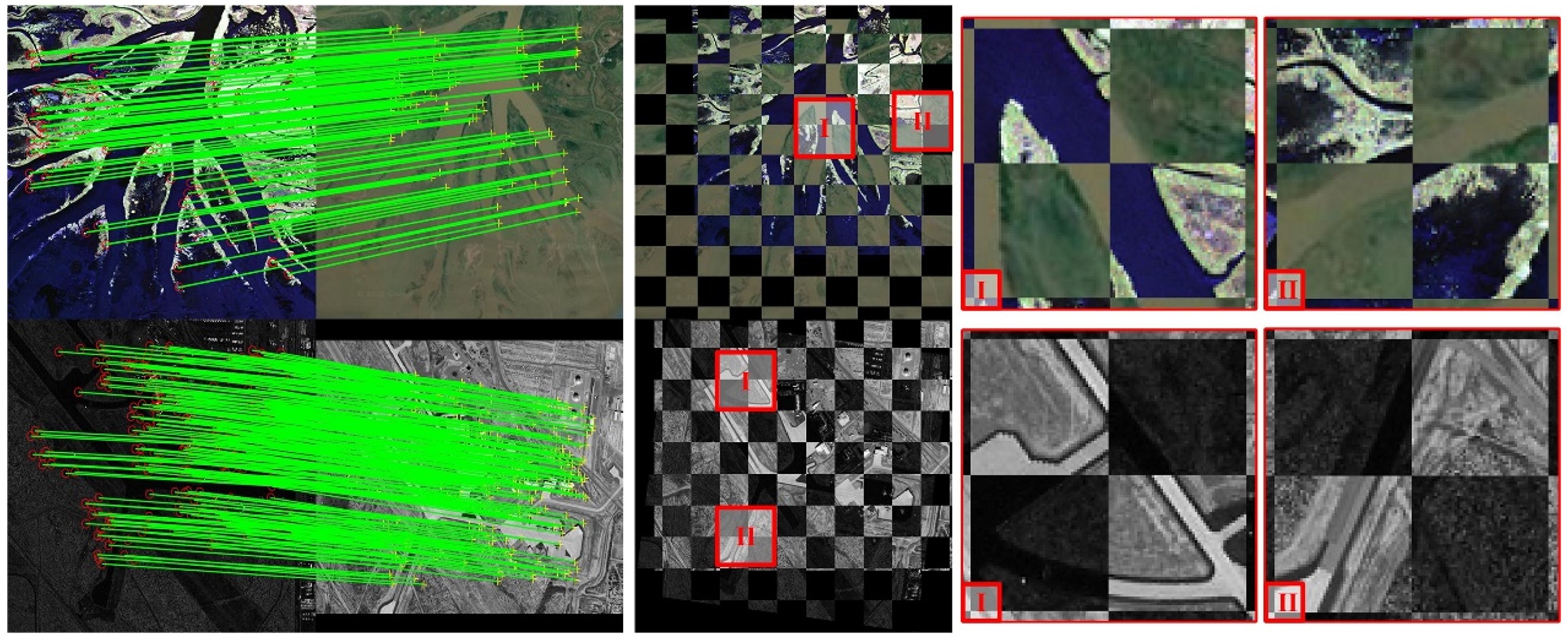
顾及各向异性加权力矩与绝对相位方向的异源影像匹配
武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021
姚永祥 张永军 万一 刘欣怡 郭浩宇
针对异源遥感影像之间存在光照差异显著、对比度差异大和非线性辐射畸变等问题所导致匹配难题,本文提出了一种顾及各向异性加权力矩与绝对相位一致性方向直方图的异源影像匹配方法。首先,利用各向异性滤波进行影像非线性扩散,在此基础上计算影像的相位一致性最大矩和最小矩,并构造各向异性加权力矩方程,求解得到各向异性加权力矩图。之后,对相位一致性模型进行扩展,建立绝对相位一致性方向梯度,并结合对数极坐标描述模板,建立一种绝对相位方向梯度直方图(histogram of absolute phase consistency gradients,HAPCG),最后利用欧氏距离作为匹配测度进行同点名识别...
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]
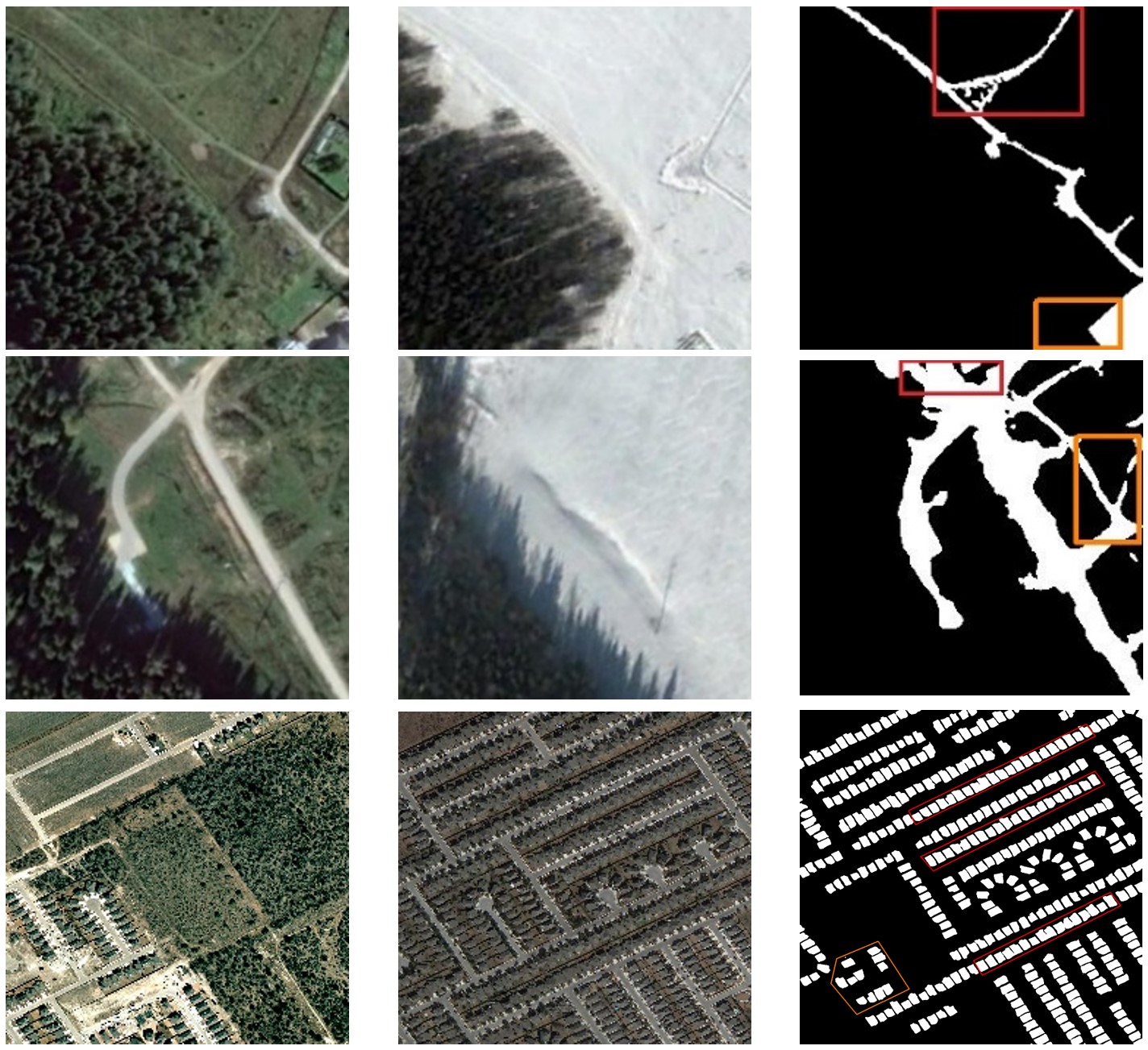

CLNet: Cross-Layer Convolutional Neural Network for Change Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Imagery
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021
Zhi Zheng, Yi Wan*, Yongjun Zhang*, Sizhe Xiang, Daifeng Peng and Bin Zhang
Change detection plays a crucial role in observing earth surface transition and has been widely investigated using deep learning methods. However, the current deep learning methods for pixel-wise change detection still suffer from limited accuracy, mainly due to their insufficient feature extraction and context aggregation. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Cross Layer convolutional neural Network (CLNet) in this paper, where the UNet structure is used as the backbone and newly designed Cross Layer Blocks (CLBs) are embedded to incorporate the multi-scale features and multi-level context information...
[code] | [related publications]
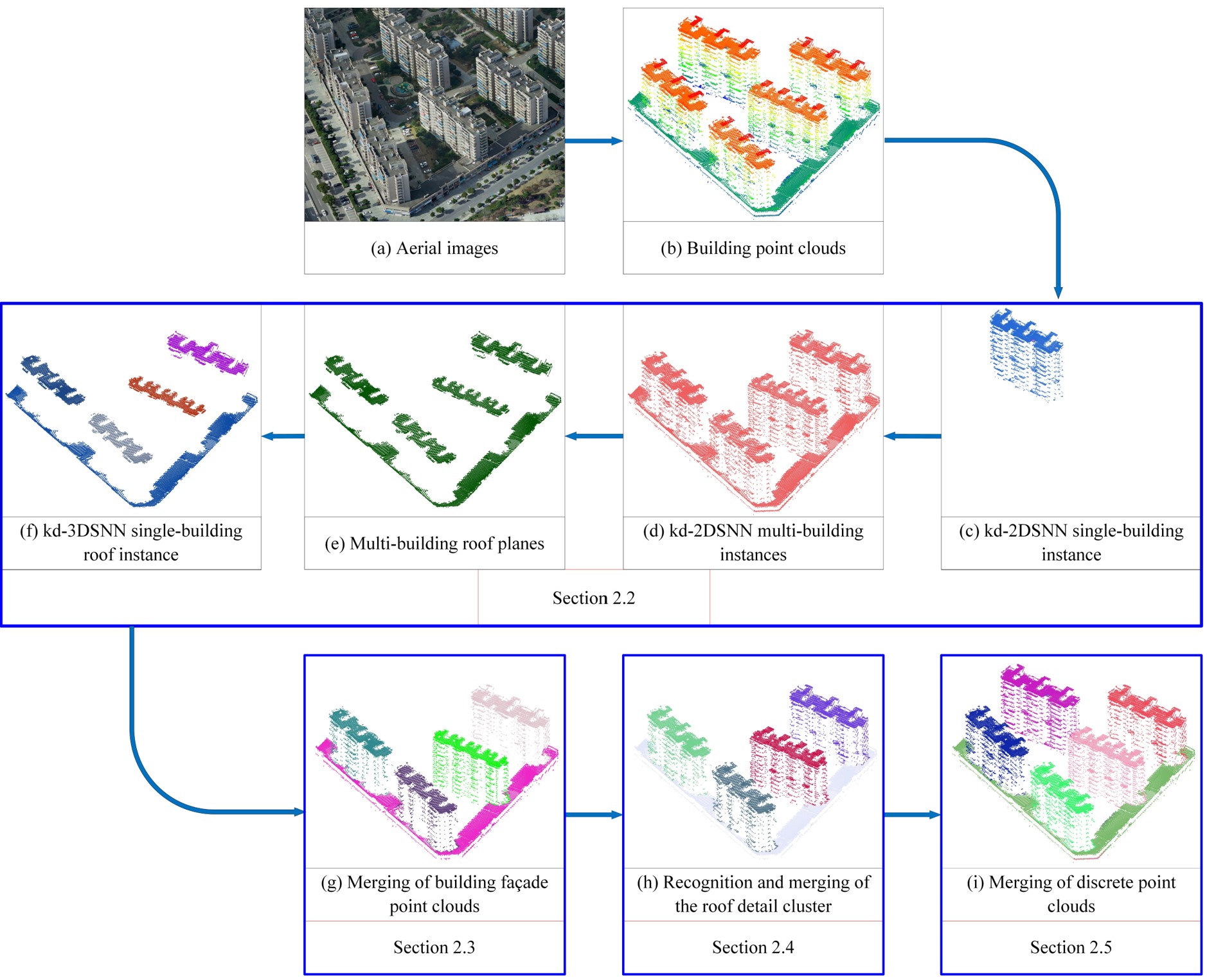
Unsupervised Building Instance Segmentation of Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds for Parallel Reconstruction Analysis
Remote Sensing, 2021
Yongjun Zhang*, Wangshan Yang, Xinyi Liu, Yi Wan, Xianzhang Zhu, Yuhui Tan
Efficient building instance segmentation is necessary for many applications such as parallel reconstruction, management and analysis. However, most of the existing instance segmentation methods still suffer from the low-completeness, low-correctness and low-quality for building instance segmentation, which are especially obvious for complex building scenes. This paper proposes a novel unsupervised building instance segmentation (UBIS) method of airborne LiDAR point clouds for parallel reconstruction analysis, which combines clustering algorithm and a novel model consistency evaluation method...
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]
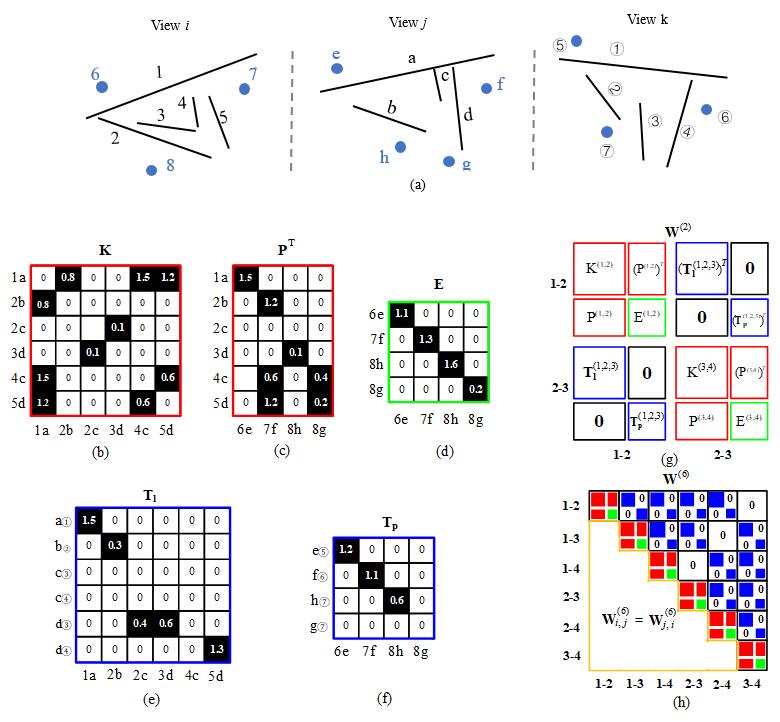
Robust line segment matching across views via ranking the line-point graph
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Volume 171, January 2021
Dong Wei, Yongjun Zhang, Xinyi Liu, Chang Li, Zhuofan Li
Line segment matching in two or multiple views is helpful to 3D reconstruction and pattern recognition. To fully utilize the geometry constraint of different features for line segment matching, a novel graph-based algorithm denoted as GLSM (Graph-based Line Segment Matching) is proposed in this paper, which includes: (1) the employment of three geometry types, i.e., homography, epipolar, and trifocal tensor, to constrain line and point candidates across views; (2) the method of unifying different geometry constraints into a line-point association graph for two or multiple views; and (3) a set of procedures for ranking, assigning, and clustering with the line-point association graph...
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [code] | [related publications]
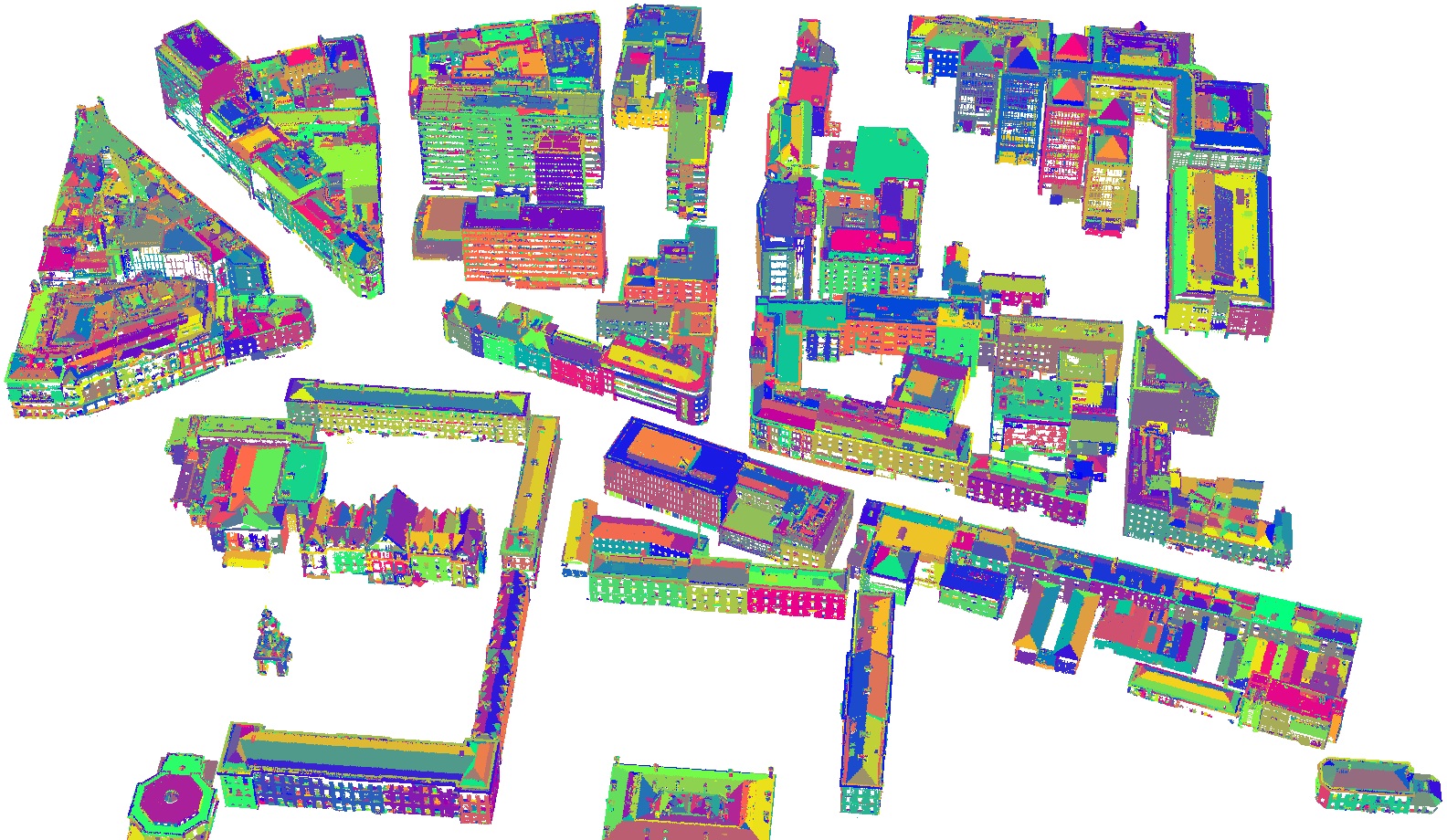
QTPS: Robust 3D plane segmentation from airborne point clouds based on quasi-a-contrario theory
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing. 2021 Jun 30;14:7133-47.
Xianzhang Zhu, Xinyi Liu, Yongjun Zhang, Yi Wan, Yansong Duan
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [code]

CoFSM: Multi-modal Remote Sensing Image Matching Considering Co-occurrence Filter
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 2022, vol.31, pp.2584-2597
Yongxiang Yao, Yongjun Zhang, Yi Wan, Xinyi Liu, Xiaohu Yan, Jiayuan Li
[Dataset] | [Demo] | [related publications]

WDCD: Accurate cloud detection in high-resolution remote sensing imagery by weakly supervised deep learning
Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 250, 1 December 2020
Yansheng Li, Wei Chen, Yongjun Zhang, Chao Tao, Rui Xiao, Yihua Tan
Cloud cover is a common and inevitable phenomenon that often hinders the usability of optical remote sensing (RS) image data and further harms the continuous cartography based on RS image interpretation. To alleviate the labor of annotating the pixel-level labels, this paper proposes a weakly supervised deep learning based cloud detection (WDCD) method using block-level labels indicating only the presence or the absence of cloud in one RS image block. ...
[Dataset] | [related publications]