Unsupervised Building Instance Segmentation of Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds for Parallel Reconstruction Analysis (UBIS)
Unsupervised Building Instance Segmentation of Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds for Parallel Reconstruction Analysis
Yongjun Zhang*, Wangshan Yang, Xinyi Liu, Yi Wan, Xianzhang Zhu, Yuhui Tan
Abstract
Efficient building instance segmentation is necessary for many applications such as parallel reconstruction, management and analysis. However, most of the existing instance segmentation methods still suffer from the low-completeness, low-correctness and low-quality for building instance segmentation, which are especially obvious for complex building scenes. This paper proposes a novel unsupervised building instance segmentation (UBIS) method of airborne LiDAR point clouds for parallel reconstruction analysis, which combines clustering algorithm and a novel model consistency evaluation method. The proposed method first divides building point clouds into building instances by improving kd-tree 2D shared nearest neighbor clustering algorithm (Ikd-2DSNN). Then the geometric feature of the building instance is obtained by model consistency evaluation method, which is used to determine whether the building instance is a single building instance or a multi-building instance. Finally, for multiple building instances, the improved kd tree 3D shared nearest neighbor clustering algorithm (Ikd-3DSNN) is used to divide multi-building instance again to improve the accuracy of building instance segmentation. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed UBIS method obtained good performances for various buildings in different scenes such as high riser, podium buildings and residential area with detached houses. A comparative analysis confirms that the proposed UBIS method performed better than state-of-the-art methods.
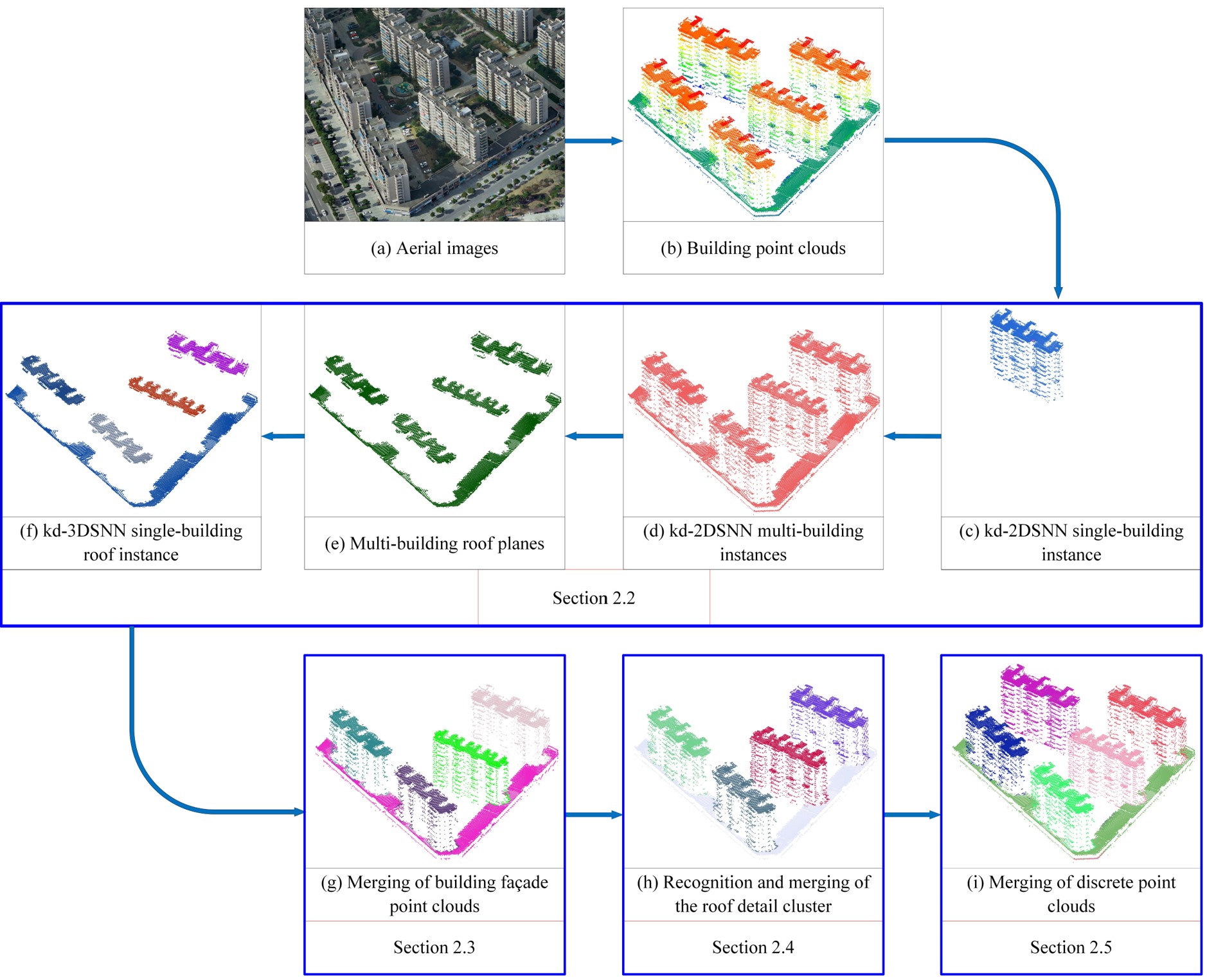
Figure 1. Workflow of the proposed UBIS method: (a) aerial images corresponding to inputted building point clouds, (b) inputted building point clouds, (c) the output of single-building instance, (d) the output of multi-building instances, (e) the output of multi-building roof planes, (f) the output of single-building roof instance, (g) the output of merging of building façade point clouds, (h) the recognition and merging of roof detail cluster, (i) the output of isolated point clouds cluster merged into building instance.
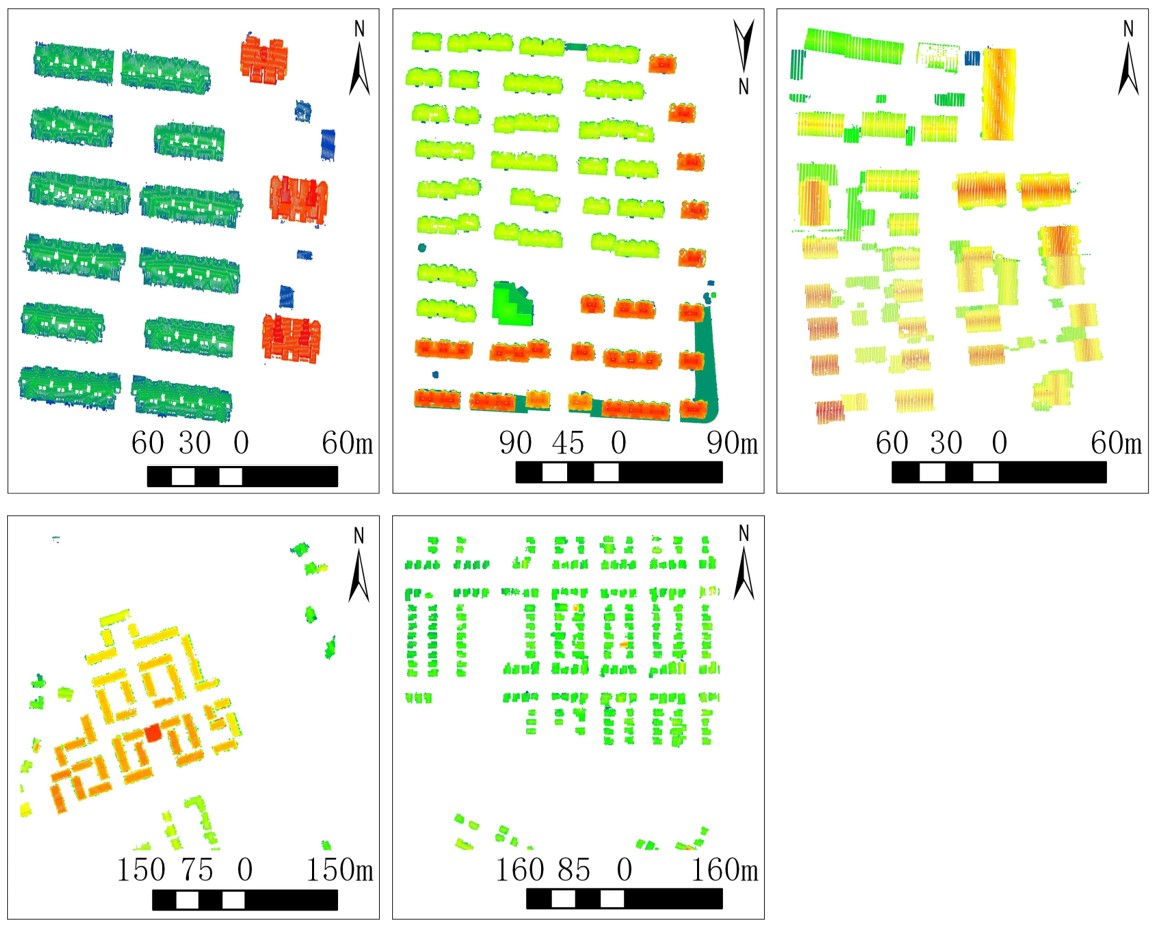
Figure 2. Dataset overview
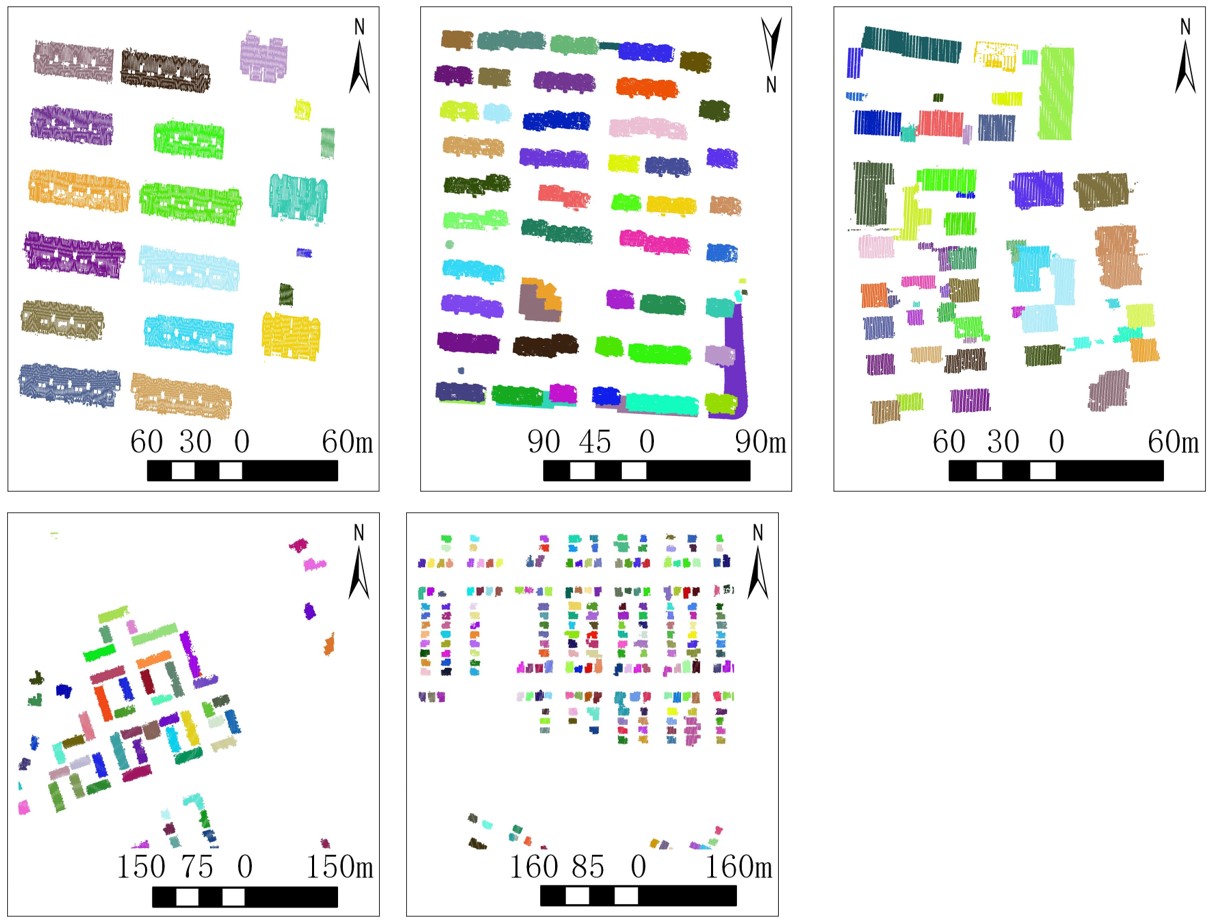
Figure 2. Results overview